Home »
Archive by category Hosting Industry (Page 2)
Ensuring the security of your website is an ongoing process that should be integrated into every aspect of its deployment, maintenance, and visitor safety. At CooliceHost, we provide website protection for various configurations, including single websites for business owners, multi-site WordPress installations, and web agencies with multiple clients....
Continue reading
August 9, 2023 admin
Cloud Hosting, Hosting Industry, Nginx Hosting, Semi-dedicated Hosting, Shared hosting, VPS - VDS
No Comment
Imagine running a business with a strong and dependable network, ensuring seamless connectivity to the Internet and between different locations. However, unexpected network outages can occur, wreaking havoc on the business’s revenue and causing considerable harm. That’s where network redundancy comes into play. It acts as a safety...
Continue reading
August 7, 2023 admin
Hosting Industry
No Comment
When monitoring metrics for eCommerce websites, it is crucial to recognize that these metrics only indicate symptoms, and various symptoms can be identified through different metrics. By tracking these metrics, you can discover various behavioral trends on your website and take necessary measures to enhance the conversion rate....
Continue reading
August 3, 2023 admin
CMSs, Hosting Industry
No Comment
If you experience multiple reinfections and your website is one among several in an account, there is a strong possibility that you are facing cross-site contamination. Cross-site contamination refers to the negative impact on a website caused by neighboring sites on the same server due to inadequate isolation...
Continue reading
July 25, 2023 admin
Hosting Industry
No Comment
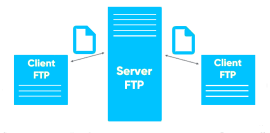
What is File Transfer Protocol (FTP)? File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a widely used method for transferring files over a network. It operates at the application layer of the OSI model and the fourth layer of the TCP model. This ensures a reliable and connection-oriented communication between the...
Continue reading
July 21, 2023 admin
Hosting Industry
No Comment
As someone who sends emails, you’ve probably heard about the importance of following email best practices to get the best results from your email program. One of these best practices is ensuring that you properly authenticate your email messages. However, understanding the three pillars of email authentication –...
Continue reading
July 18, 2023 admin
Cloud Hosting, Hosting Industry, Nginx Hosting, Shared hosting
No Comment
When it comes to building a website, you’ll need a lot of files and folders. And if you’re working on a complex website, it can feel like the number of files and folders is never-ending. This can be especially overwhelming for developers and designers. You might find yourself...
Continue reading
July 14, 2023 admin
CMSs, Hosting Industry
No Comment
When you’re choosing a network carrier for your dedicated server, it’s an important decision to make. Understanding your options fully is key. The difference between premium carriers and budget carriers often comes down to their global reach, reliability, and level of service. During the selection process, you may...
Continue reading
July 11, 2023 admin
Hosting Industry
No Comment
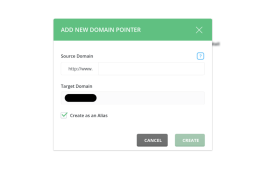
In the world of web hosting, the use of domain aliases has become increasingly common. Whether you are managing your own website or providing hosting services to clients, understanding domain aliases is vital to ensure smooth functioning and enhance user experience. In this article, we will explore the...
Continue reading
July 5, 2023 admin
CMSs, Hosting Industry
No Comment
Redis Object Cache works by storing frequently accessed objects in memory for fast retrieval, reducing the need to fetch the objects from the original data source (such as a database) repeatedly. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how Redis Object Cache typically operates: Application requests an object: When an...
Continue reading
June 9, 2023 admin
Cloud Hosting, Hosting Industry, Nginx Hosting, Semi-dedicated Hosting, Shared hosting, VPS - VDS
No Comment