An inode represents every single file, directory and symlink in the hosting account.
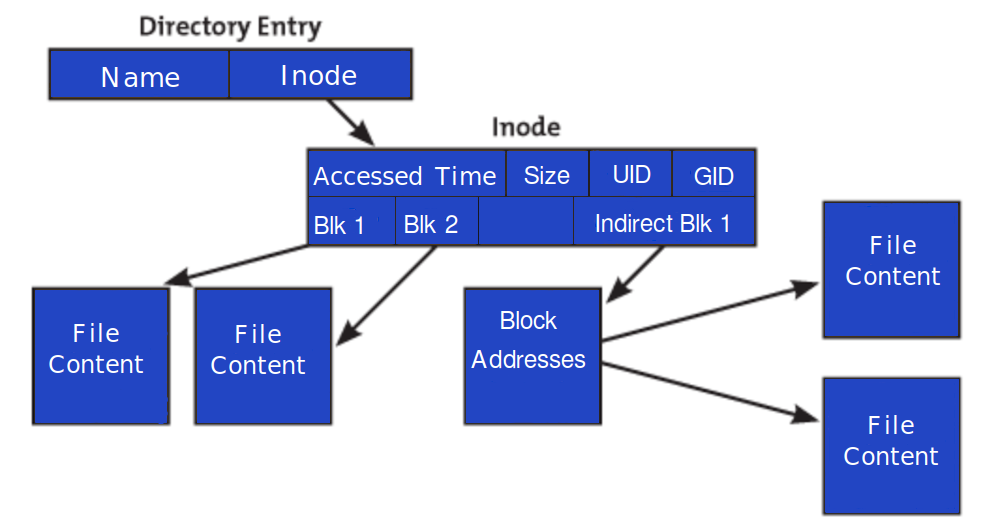
An inode (index node) is a fundamental concept in the Linux/UNIX file system. Each object in the file system is represented by an Inode.
Every file in a Linux/UNIX environment has the following attributes:
- a: append only
- c: compressed
- d: no dump()
- e: extent format
- i: immutable
- j: data journalling
- s: secure deletion
- t: no tail-merging
- u: undeletable
- A: no atime updates
- C: no copy on write
- D: synchronous directory updates
- S: synchronous updates
- T: top of directory hierarchy
All the above information is stored in Inode. In short, the Inode identifies the file and its attributes. Each Inode is identified by a unique number within the file system.
An inode is also known as an index number. An inode is an internal data structure that Linux/UNIX uses to store information about file system objects.
What is the number of inodes offered with the hosting plans?
The number of inodes available with the hosting plans are as follows:
Web Hosting:
– Webmaster Mini – 250 000 Inodes
– Webmaster – 500 000 Inodes
– Big Dog – 750 000 Inodes
– Big Dog 2 – 1 000 000 Inodes
Cloud Hosting:
– Cloud 2G – 500 000 Inodes
– Cloud 4G – 750 000 Inodes
– Cloud 6G – 1 000 000 Inodes
– Cloud 8G – 1 500 000 Inodes
Reseller Hosting:
– Baby – 3 932 160 Inodes
– Business – 7 864 320 Inodes
– Ultimate – 15 728 640 Inodes
– Enterprise – 31 457 280 Inodes
VDS:
– Based on the custom solution and storage
Where can I find information on how many Inodes my hosting account has?
What do I do if the number of files and directories exceeds my plan?
If the number of Inodes in your account is too high, you should try to determine the reason as quickly as possible so that you can reduce the value within the limit of your hosting plan.
Most often, the increased number of inodes is from accumulated cache files from the systems themselves, installed on the account, various logs and temporary files. It is recommended that you review the content of the account and remove any redundant information (including systems that are not in use).
Some common reasons for a high number of Inodes are:
Cron jobs
Running Cron jobs or other automated processes can create a huge number of files in a very short time. Modify/disable the cron task (if such a connection is found) or delete unnecessary files. Also, you can disable generating logs or mails that are mostly sent to your webmail service in the same hosting account.
Undeleted messages
Old messages in users’ mailboxes are often not deleted from the Trash folder (we’ve seen over 15 GB of old mail in the trash!). You can download these messages to your local computer (if you want to keep them), then delete them from the server.
Service directories
Other directories where files are commonly forgotten are /tmp, /logs, /cache – the small file size of these directories is usually deceiving – 100MB of disk space can contain 40000 text files (Inodes).
In case the number of files and directories cannot be reduced to the value for the used plan, an option is to switch to the next hosting plan or a separate server.